Dental fluorosis is a cosmetic condition resulting from excessive fluoride intake during tooth development. It does not affect the health and function of the teeth but it changes their appearance. Understanding and identifying the condition is important to take the necessary measures to prevent them and avoid any psychosocial effects that may occur in the future. The blog focuses on dental fluorosis causes, signs, and advanced treatment options.
What is dental fluorosis?
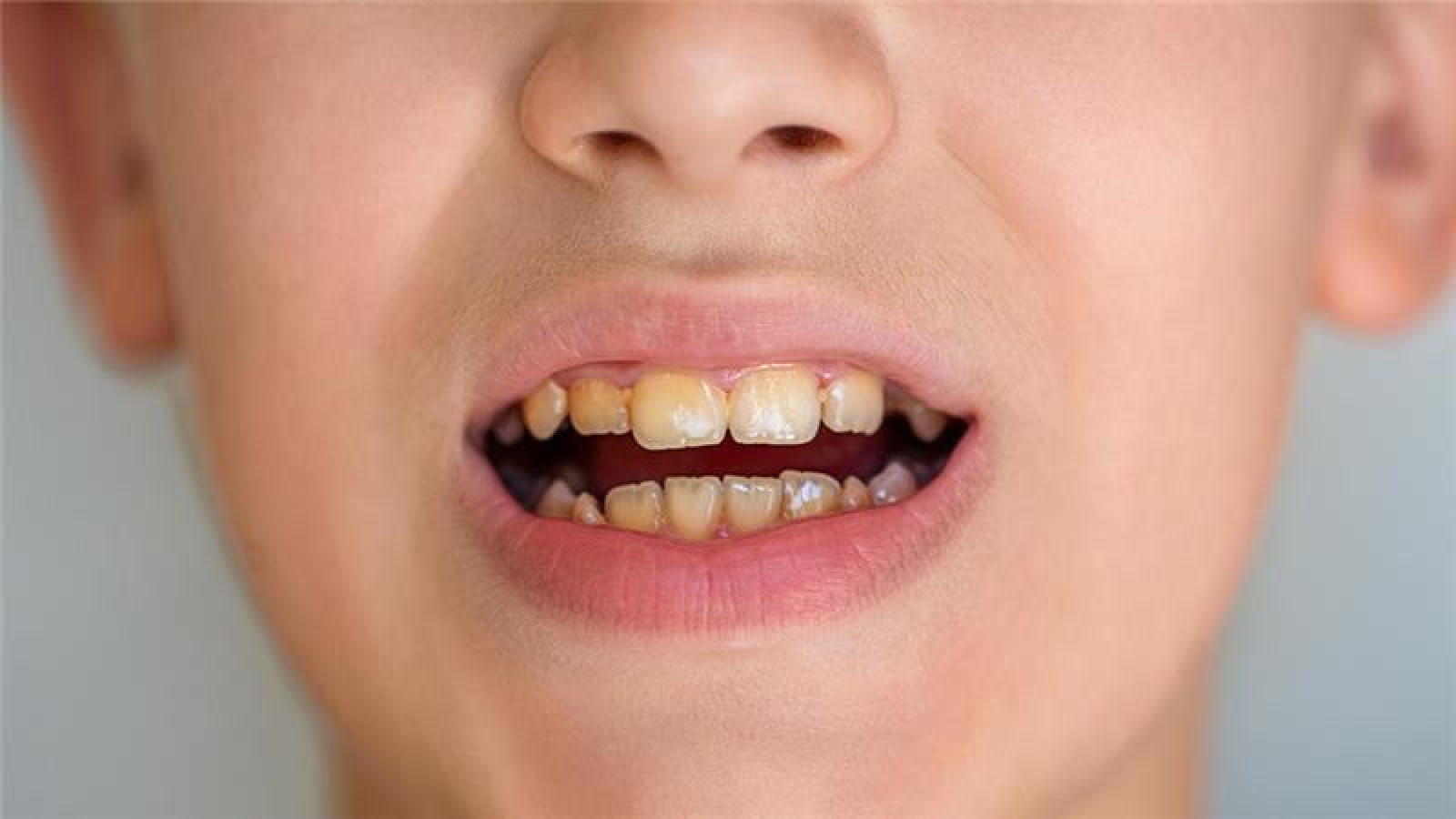
Dental fluorosis usually occurs at the age of (0-8) while the teeth are developing. It affects tooth enamel by causing hypomineralization and causing white spots or streaks, mild discoloration, brown stains and even pitting or surface irregularities. So, enamel can become more porous. However, it doesn’t affect enamel strength.
Dental fluorosis is of three types – mild, moderate and severe. Mild fluorosis appears as faint white streaks or specks and covers less than 25% of the tooth surface. They are the most common and least concerned. Moderate fluorosis has more distinct white patches and covers up to 50% of the tooth surface. Pitted, rough, and porous enamel indicates severe fluorosis and affects most teeth.
Causes of dental fluorosis
Dental fluorosis is caused by excessive fluoride consumption during the period of teeth development. Common sources of fluoride are drinking water with a high fluoride content, swallowing too much fluoride toothpaste, and taking fluoride supplements. Certain foods and beverages may also cause dental fluorosis. Other risk factors include genetics, diet and geographical regions.
Signs and symptoms of dental fluorosis
Tooth discoloration is a symptom of dental fluorosis. It can vary according to severity and disappear once teeth erupt. Dentists categorize these into three:
Mild Fluorosis
Characterized by:
- Faint white streaks or specks
- Small opaque patches on the enamel
- Usually visible only in bright light
- No changes in the tooth structure
This is the most common form and often goes unnoticed.
Moderate Fluorosis
More visible than mild fluorosis:
- Brown or yellow stains
- Noticeable white patches
- Slight surface irregularities or roughness
- Affects a large portion of the tooth surface
- The enamel may appear blotchy or uneven.
Severe Fluorosis
The most advanced form with clear structural changes:
- Pitting of the enamel (small dents or holes)
- Enamel erosion or loss of the outer layer
- Pronounced dark brown stain
- Teeth may appear rough, chalky, or porous
This form requires cosmetic dental treatment to improve its appearance.
Usually, fluorosis does not affect the function and strength of teeth. But when the enamel becomes porous, the teeth get sensitive and the chance of them being stained increases. Visible discolouration can damage the confidence of a child. The majority of people take dental fluorosis treatment for aesthetic reasons than to health concerns.
Advanced treatment options for dental fluorosis
Mild dental fluorosis doesn’t need any treatment but in moderate and severe cases cosmetic or restorative treatments are done to improve the appearance of affected teeth.
Cosmetic treatments
1. Teeth whitening/bleaching
Teeth whitening techniques are used to lighten moderate fluorosis stains, especially white spots and brown discoloration. Unlike other methods, professional teeth whitening treatment is safe and effective.
2. Microabrasion
This technique involves removing a thin layer from the enamel to reduce white spots and uneven surfaces. It is often done with teeth whitening.
3. Veneers and bonding
Dental bonding: A tooth-coloured resin is placed over the tooth to cover the stains.
Porcelain veneers: Ceramic shells placed on the front surface of teeth to hide discoloration and pitting.
Preventive Approaches
Fluoride management for children is very important. This includes using the right amount of toothpaste, avoiding drinking water with high fluoride levels and not taking fluoride supplements.
Educating parents about fluorosis is crucial to preventing this issue in children. So that they can guide children to use a pea sized amount of toothpaste and not swallow while brushing.
Advanced treatments for severe cases
1. Crowns or restorations
Dental crowns can restore strength and aesthetics in cases of severe pitting, enamel erosion and structural defects. These restorations fully cover the tooth, protecting it and improving its appearance.
2. Minimally invasive enamel replacement techniques
Damaged enamel can be removed and replaced with high-strength restorative materials. These techniques help preserve the natural structure of teeth.
Preventing Dental Fluorosis
Safe fluoride use in children.
Use a pea-sized amount of toothpaste for ages 3–6.
- Teach children to spit toothpaste instead of swallowing it.
- Avoid unnecessary fluoride supplements unless recommended by a dentist.
Monitoring fluoride levels in drinking water
- Check the fluoride concentration in the local water supply.
- If water fluoride content is above recommended levels, consider alternatives like filtered or bottled water.
- Be mindful of your total fluoride intake from water, food, and dental products.
Choosing appropriate dental products
- Select age-appropriate children’s toothpastes with safe fluoride concentrations.
- Avoid using adult-strength toothpaste for young kids.
- Look for ADA- or dentist-approved fluoride products.
- For families in high-fluoride areas, consider low-fluoride toothpaste if advised by a dentist.
Dental fluorosis is a cosmetic condition caused by excess fluoride intake during early childhood, and its signs can range from mild white streaks to severe enamel pitting and discoloration.
Understanding the causes, recognizing early symptoms, and being aware of the available cosmetic and advanced treatment options can help parents make decisions about their child’s oral health.
Contact Dr Bobby Dental Clinic for expert and personalised oral care. We provide the best fluorosis treatment for children who face the issue. Visit our website to know more about the treatments we offer.
Mild dental fluorosis may become less noticeable over time as teeth naturally wear and stain. However, it does not completely disappear on its own, and cosmetic treatments are often needed for visible improvement.
Dental fluorosis is primarily a cosmetic condition and does not affect the health or function of the teeth. Even in moderate cases, the teeth remain strong, though severe fluorosis may cause surface irregularities.
Fluorosis is not caused by a vitamin deficiency. It occurs due to excessive fluoride intake during tooth development, not due to a lack of vitamins.
One common symptom of dental fluorosis is the presence of white streaks or spots on the enamel of the teeth.
For fluorosis, a low-fluoride toothpaste or a mild whitening toothpaste recommended by a dentist is best. In moderate or severe cases, professional treatments are more effective than toothpaste alone.